Knee pain is a widespread issue that can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. Whether you’re dealing with an injury, a medical condition, or the effects of daily wear and tear, knee discomfort can greatly impact your daily life. The good news is that there are various causes and ways to manage knee pain effectively, providing relief and improving your overall quality of life.
Knee pain can have diverse origins, and it’s important to grasp the underlying reasons to effectively manage it. Some common culprits behind knee pain include:
Osteoarthritis: A joint condition that causes cartilage to break down over time.
Ligament injuries: Tears or strains in the ligaments, such as the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) or PCL (posterior cruciate ligament).
Meniscus tears: Damage to the meniscus, the protective cartilage within the knee.
Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the knee.
Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint.

Recognizing when to consult a medical specialist is crucial when dealing with knee pain. It’s advisable to seek expert guidance if you experience:
To pinpoint the root cause of knee pain accurately, healthcare professionals may employ various diagnostic tools, including:
X-rays: These reveal bone structure and any signs of arthritis or fractures.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Offers detailed images of soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
CT scan (Computed Tomography): Provides a 3D view of the knee joint for precise evaluation.
Ultrasound: Useful for examining soft tissues and identifying issues like fluid buildup or inflammation.
Blood tests: May be conducted to rule out inflammatory or autoimmune conditions contributing to knee pain.
When it comes to managing knee pain, a wide range of options is available, catering to various needs and preferences. These options encompass both home-based remedies and professional interventions, ensuring that you can find the most suitable approach for your specific situation.
Rest and ice: Begin by giving your knee ample rest and applying ice packs to reduce swelling and discomfort.

Elevation: Elevating your leg can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications: Non-prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can provide temporary relief.
Topical creams: Creams or ointments with anti-inflammatory properties may offer localized pain relief.
Customized exercise programs: A physical therapist can create a tailored exercise regimen to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance joint stability.
Manual therapy: Hands-on techniques like massage or manipulation can alleviate pain and improve joint mobility.
Modalities: Therapists may use modalities like ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or hot/cold treatments to manage pain and inflammation.
Medications play a crucial role in treating knee pain by providing relief from discomfort and managing inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen are commonly used to alleviate pain and reduce swelling. Acetaminophen is another option for pain management, although it doesn’t possess the anti-inflammatory properties of NSAIDs. In cases where stronger pain relief is necessary, healthcare providers may prescribe medications tailored to individual needs, considering factors like the severity of pain and the patient’s overall health. It’s essential to use such medications under medical guidance, as they can have side effects and interactions with other drugs. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most suitable medication regimen for addressing knee pain effectively and ensuring the best possible outcome for the patient’s condition.
Interventional pain management can be a good alternative treatment for patients who are not candidates for prosthetic surgery or who want to avoid more invasive procedures. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider to determine if interventional pain management is a good option for your specific condition.
Corticosteroid injections: These injections can help reduce inflammation and pain in the knee join.
Viscosupplementation: Hyaluronic acid injections can help lubricate the knee joint, reducing friction and pain.
Radiofrequency ablation: A minimally invasive procedure that uses heat to disrupt pain signals from nerves around the knee.

Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy: PRP injections use your own blood components to stimulate healing and reduce pain.
Stem cell injections: This treatment involves injecting stem cells into the knee joint to promote healing and reduce pain.
Braces and supports can be used to help manage knee pain. Here are some types of braces and supports that can be used:
Knee braces: Knee braces can be used to provide support and stability to the knee joint. They can also help reduce pain and inflammation by unloading the joint. Knee braces can be rigid or flexible, and they can be worn during physical activity or throughout the day.
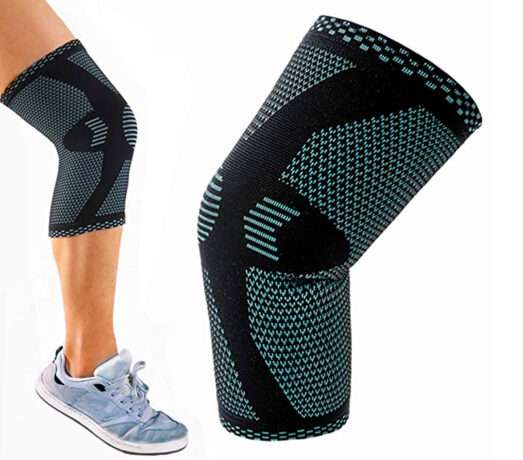
Knee sleeves: Knee sleeves are a type of knee brace that are made of a stretchy material and provide compression to the knee joint. They can help reduce pain and inflammation and provide support to the knee during physical activity.

Foot/ankle orthoses: Foot/ankle orthoses are medical devices that can be added to a person’s body to support, align, position, immobilize, prevent or correct deformity, assist weak muscles, or improve function. They can be used to decrease pain, improve physical function, and possibly slow disease progression in individuals with osteoarthritis of the knee.
Compression sleeves: Compression sleeves can be used to provide compression to the knee joint, which can help reduce pain and inflammation. They can also help improve blood flow and provide support to the knee during physical activity.
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider to determine if a brace or support is a good option for your specific condition. They can help you choose the right type of brace or support and ensure that it is fitted properly.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the load on your knees and decrease pain.
Activity modification: Adjusting your daily activities to minimize high-impact movements or using assistive devices when necessary.
Ergonomic changes: Ensuring your work and living environments are knee-friendly, with appropriate seating and support.
Surgical options for knee pain include:
Knee replacement surgery: This procedure involves resurfacing a knee damaged by arthritis by replacing the damaged parts of the knee joint with an artificial joint.
Knee arthroscopy: This procedure involves inserting a small camera into the knee joint to diagnose and treat problems such as torn meniscus, damaged articular cartilage, and inflamed synovial tissue.
Cartilage repair: This procedure involves repairing damaged cartilage in the knee joint using various techniques such as microfracture, autologous chondrocyte implantation, and osteochondral autograft transplantation.
Osteotomy: This procedure involves cutting and reshaping the bones in the knee joint to shift weight from the damaged part of the joint to a healthier part.
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider to determine if surgery is a good option for your specific condition. They can help you choose the right type of surgery and ensure that you are fully informed about the risks and benefits of each procedure.
The choice of treatment option will depend on the severity of your knee pain, its underlying cause, and your overall health. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate approach to manage your knee pain effectively and improve your quality of life.
In conclusion, knee pain is a common issue that can affect anyone, but there are various causes and effective ways to manage it. Consulting with a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan can help you regain comfort and mobility in your daily life. By taking proactive steps, you can work towards a healthier, pain-free future for your knees.