What Is A Migraine? Current Approaches In The Treatment Of Migraine
What is a migraine?
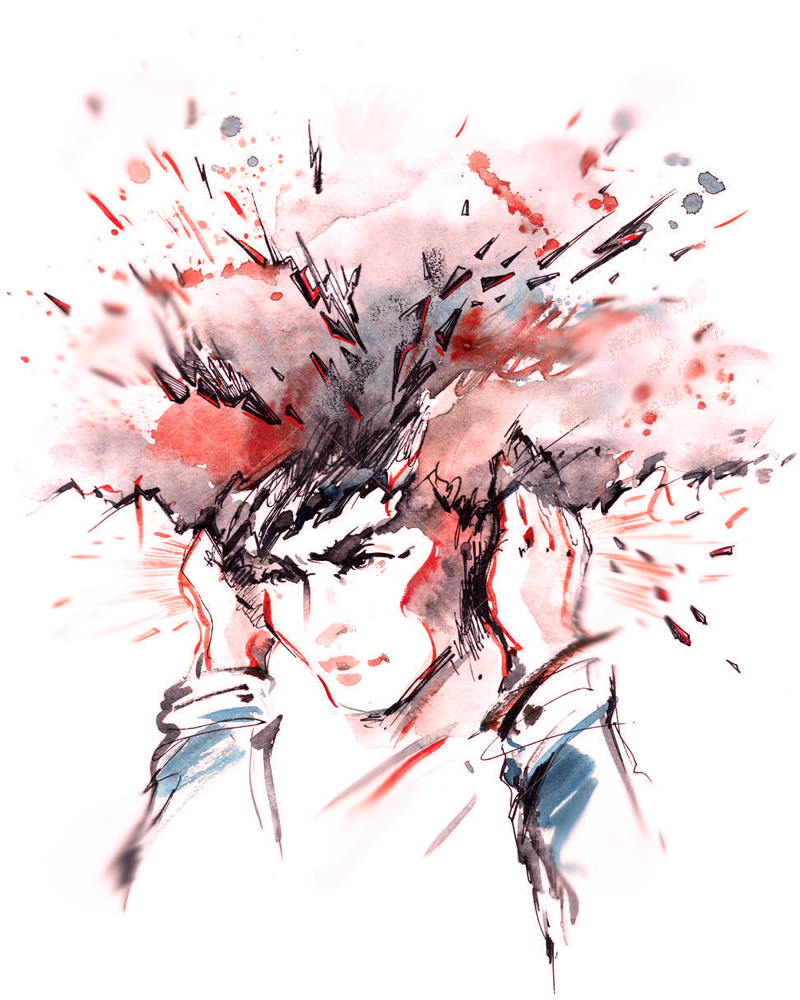
Migraine is a disease as old as human history. This type of headache is a very important health problem for the society. It is a type of headache that tends to recur and causes moderate to very severe pain. The pain is usually described as throbbing or pulsating and usually begins on one side of the head. Migraine headaches get worse with physical activity, light, sound, or physical movement.

If left untreated, a migraine headache attack typically lasts from 4 hours to 3 days. Patients may be sensitive to light, sound and even smell and may also experience nausea and/or vomiting. Some of the patients may feel that the pain will come 5-60 minutes before the presence of warning signals known as aura from pain attacks. Migraine is not a life-threatening brain disease. After the diagnosis of migraine, the treatment of the patient should be done according to a certain order and in cooperation with the physician.
Current approaches in the treatment
In migraine attacks, resting in a dark and quiet room with an ice pack can help reduce the pain. If sleep is possible, the patient usually wakes up free of pain. For the prophylaxis of attacks, the frequency of pain can be reduced by some simple measures such as avoiding the factors that trigger the disease, not skipping meals, and ensuring regular sleep times.
Medications for migraine treatment
Medications in migraine is given in two ways as “prophylactic” or preventive treatment to prevent attacks, and “attack (acute headache) treatment” to relieve symptoms of an attack such as pain, nausea and vomiting. Prophylactic treatment is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of pain by using regular medications for a certain period of time. Migraine treatment is a form of treatment in which the same treatment is not applied to everyone. And each patient diagnosed with migraine should be given a special decision.
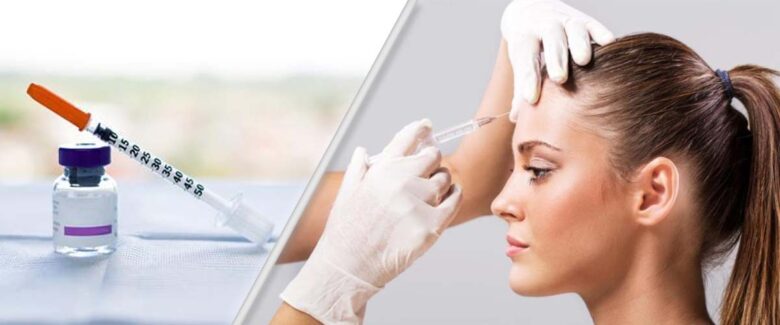
Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies (erenumab, galcanezumab, fremanezumab), popularly known as migraine vaccine, are approved for use in the preventive treatment of migraine. Although it is called a ‘vaccine’ because it is an antibody, it does not make it completely protected from the disease once it is made, like the vaccines we know in the classical sense. In fact, it is more accurate to define it as a medicine, not a vaccine.
Interventional treatments
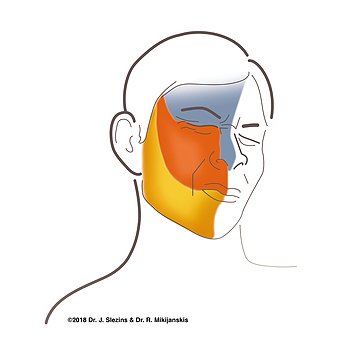
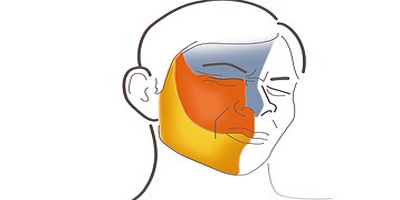
Botulinum neurotoxin is used in chronic migraine prophylaxis. Although there is not enough evidence showing its effectiveness in the treatment of episodic migraine, it can be recommended in some clinics. Local anesthetics and greater occipital nerve (GON), lesser occipital nerve (LON), supraorbital nerve (SON) blockade, and sphenopalatine ganglion blockade are among the safe and effective interventional treatments in migraine with frequent attacks, especially chronic migraine.
Neuromodulation
Different neuromodulation (stimulation of the nervous system) methods can be used in the treatment of migraine. There is experience in the treatment of migraine with both invasive and non-invasive methods. Non-invasive methods include transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial direct current stimulation, and non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation (VSS); invasive methods include occipital nerve stimulation and implanted VSS. It has no routine clinical use yet.
What is a migraine headache diary?
A migraine headache diary is a written or digital log where individuals can record detailed information about their migraine episodes. It serves as a personal record that helps track and monitor various aspects of migraines, including the frequency, duration, intensity of pain, triggers, and associated symptoms. The diary may also include information about medication usage, lifestyle factors, sleep patterns, and any remedies or interventions tried during a migraine attack.
By consistently maintaining a migraine headache diary, individuals can identify patterns and potential triggers, recognize early warning signs, and track the effectiveness of different treatments or lifestyle modifications. The diary acts as a useful tool for both individuals and healthcare professionals, providing valuable information for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and improved management of migraines.
If you’re looking to better understand your migraine headache condition and track your symptoms, “The Migraine Detective: A 30-Day Diary For Solving The Mystery Of Your Headaches” is an affordable option designed by Tural Bayramov, MD.